Driver Drowsiness Detection using Computer Vision in Matlab
Driver Drowsiness Detection using Computer Vision in Matlab
Review from Client ->
- Each year hundreds of people lose their lives due to traffic accidents around the world. Unfortunately, Iran ranks first in the world in terms of road fatalities and each year approximately thirty thousands of fellow countrymen lose their lives in these events.
- In a study by the National Transportation Research Institute (NTSRB) in which 107 random car accidents had been selected, fatigue accounted for 58% of the all accidents. A main cause of fatigue is sleeplessness or insomnia.
- Ad hoc networks were the first systems to develop the automatic navigation in cars. A noticeable weakness of these systems is that their responses to environmental changes is not real time.
- It is especially important in driving where time is a critical factor in driver’s decision. On the other hand, another method to check the driver fatigue is monitoring the physical condition and facial expressions of the drivers, which wireless sensor networks are unable to process and transmit these information with adequate precision.
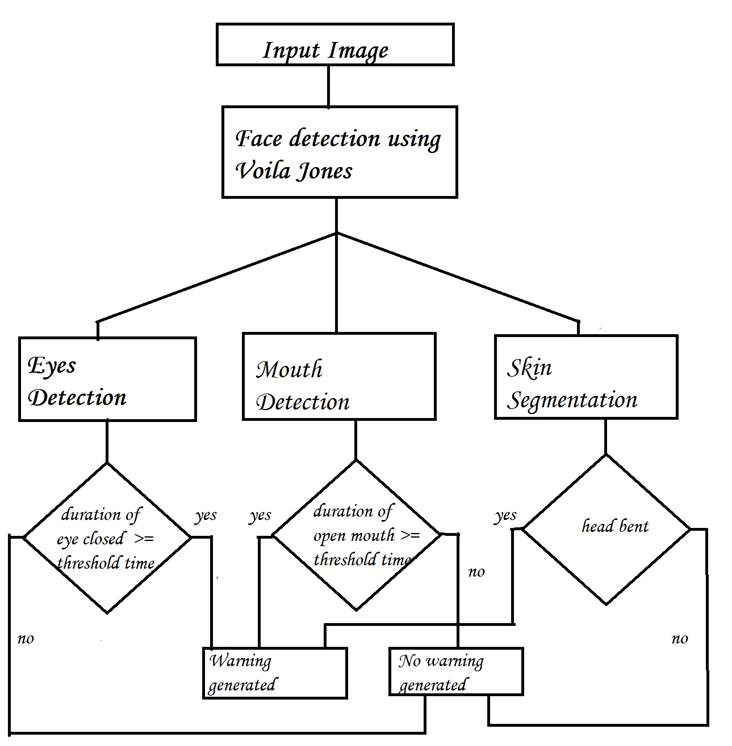
Model :
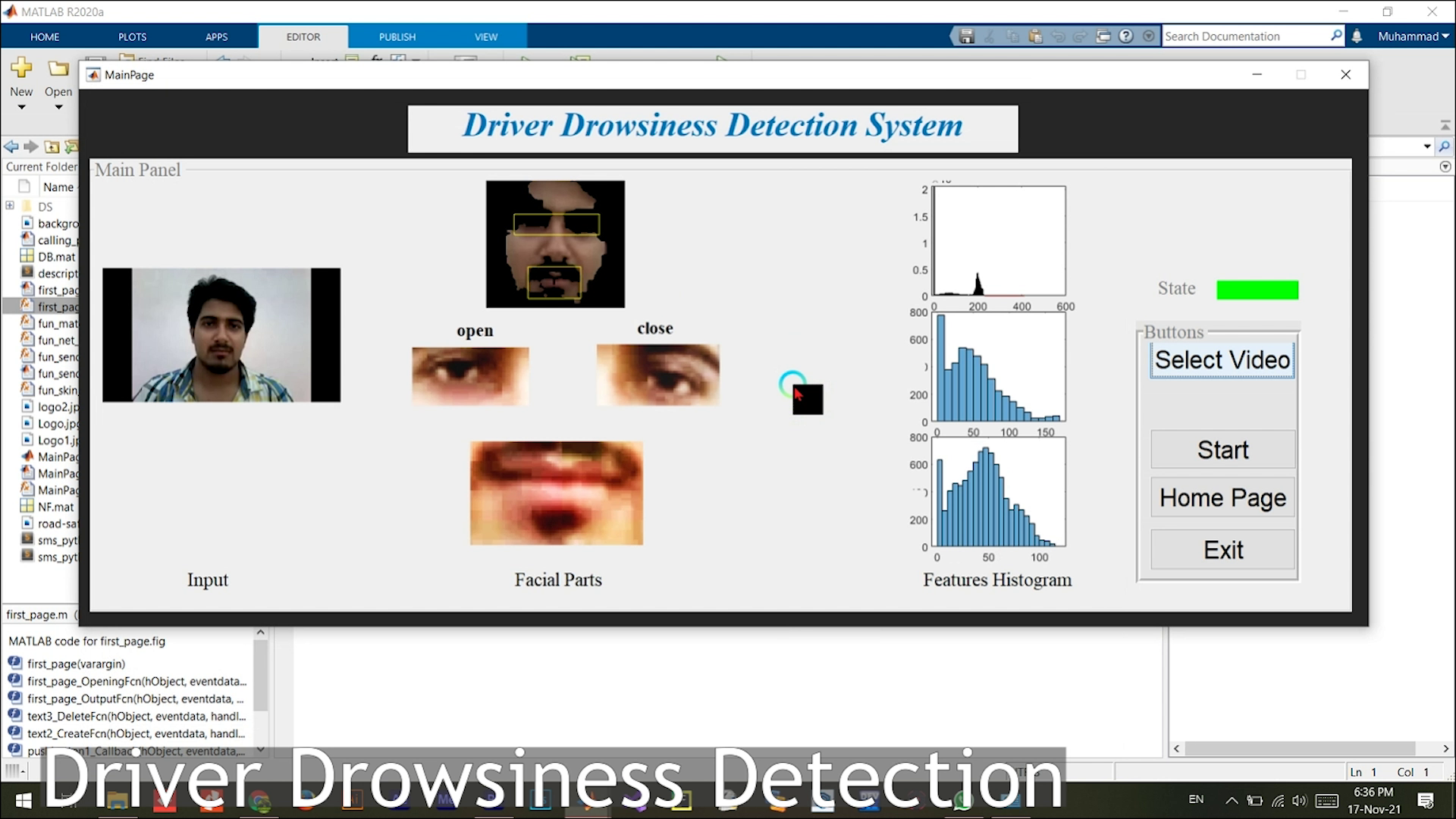
GUI:
Software Requirments:
The whole system is implemented on MATLAB.
Working Screenshots:
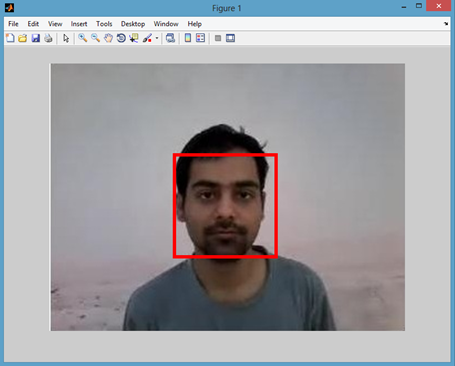
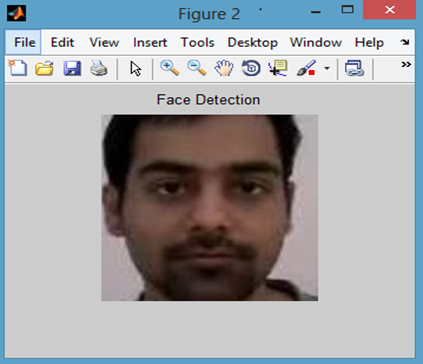 (a) Face Region after Voila-Jones algorithm is applied. (b) Cropped face region.
(a) Face Region after Voila-Jones algorithm is applied. (b) Cropped face region.
Eye Detection
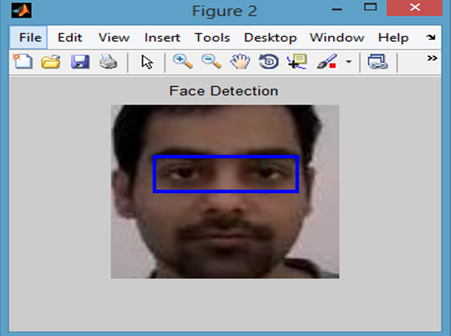
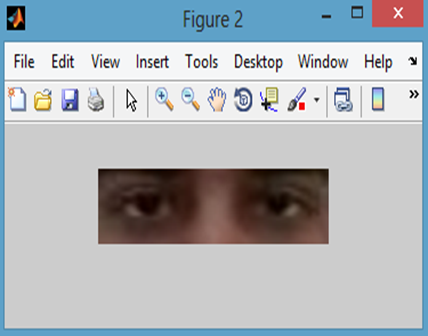
(a) Eye Region After the Calculations (b) Cropped Eye Region.



(a) Image after converting to YCbCr (b) Image after converting to grayscale (c) Image after converting to binary image



 Original Cropped eyes.
Original Cropped eyes.
Mouth Detection

 (a) Region of Mouth to be Extracted (b) Cropped Image Region.
(a) Region of Mouth to be Extracted (b) Cropped Image Region.


(a) Mouth region converted to YCbCr colour space.(b) After converting to grayscale image. (c)After converting to binary image




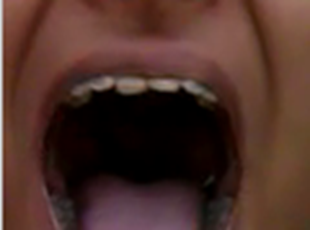

Skin Segmentation
- An image which taken inside a vehicle includes the driver’s face. Typically a camera takes images within the RGB model (Red, Green and Blue). However, the RGB model includes brightness in addition to the colours. When it comes to human’s eyes, different brightness for the same color means different colour.
- When analyzing a human face, RGB model is very sensitive in image brightness. Therefore, to remove the brightness from the images is second step. We use the YCbCr space since it is widely used in video compression standards .
- Since the skin-tone color depends on luminance, we nonlinearly transform the YCbCr colour space to make the skin cluster luma-independent. This also enables robust detection of dark and light skin tone colours. The main advantage of converting the image to the YCbCr domain is that influence of luminosity can be removed during our image processing.
- In the RGB domain, each component of the picture (red, green and blue) has a different brightness. However, in the YCbCr domain all information about the brightness is given by the Y component, since the Cb (blue) and Cr (red) components are independent from the luminosity.
Conversion from RGB to YCbCr
Cb = (0.148* Red) - (0.291* Green) + (0.439 * Blue) + 128; Cr = (0.439 * Red) - (0.368 * Green) – (0.071 * Blue) + 128;
Conversion from RGB to HSV
I’ = rgb2hsv (I);

 (a) Input Image (b) Segmented Image from Input Image
(a) Input Image (b) Segmented Image from Input Image






Decision Making
- The first frame is used for learning. All the results are calculated taking first frame as ideal frame.
Eyes Closed
When eyes are closed, the number of black pixels in binary image decreases considerably. If eyes are found closed for atleast 2 consecutive seconds (i.e. 2 * 16 = 32 frames, considering 16 frames per second), then the warning will be generated.
Mouth Open
When mouth is open, the resulting black pixels in binary image can be considerably larger or smaller than the ideal frame. The difference can be more than 6% of the black pixels in ideal frame.If mouth is found open for atleast 2 consecutive seconds (i.e. 2 * 16 = 32 frames, considering 16 frames per second), it means that the person is yawning and in response the warning will be generated.
Head Lowering
If the head is lowered, or turned around the number of skin pixels considerably decrease as compared to the ideal frame.If head is found lowered or found turned in other directions for atleast 2 consecutive seconds (i.e. 2 * 16 = 32 frames, considering 16 frames per second), it means that the person is vulnerable for accident and in response the warning will be generated.
Limitations of the algorithm.
- Objects in the video, should be uniformly illuminated, else results can differ.
- Changing distance of person from the camera can cause problems.
- Head lowering can give abrupt results in case of bald person.
- The algorithm doesn’t work for the people sleeping with eyes open.
- Face symmetry calculations are not same for everyone. The calculations considered are true for most of the people.
Accuracy
The algorithm gives correct answer on about 25 videos that makes it about 83.33% accurate
